This document describes tags used to design and implement interactive
forms on a web page.
This table:
| Support: |
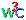 2.0,
3.0, 3.2 2.0,
3.0, 3.2 |
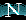 1.1+ 1.1+ |
 1.0+ 1.0+ |
and these icons:




alert you to tags and attributes that are not supported by all
browsers.
<BLOCKQUOTE> text </BLOCKQUOTE>

<BQ> text </BQ>

<BQ CLEAR = attributes>
text </BQ>

<BQ NOWRAP> text </BQ>
The block quote tag defines text that is quoted from elsewhere.
Many
browsers (including Netscape) display it in an indented block
surrounded by blank lines. Other suggestions from the HTML 2.0 spec
include displaying the text in italics or starting each line with the
Usenet standard quote indicator,
>. In HTML 3.0, the
CLEAR attribute is used to position a quote after a graphic: it can be
LEFT,
RIGHT, or
ALL and
specifies which margin should be clear. The
NOWRAP
attribute stops the
browser from wrapping except at a BR
tag.
<CENTER> text</CENTER>
The center tag defines text that should be centered.
<H1> text </H1>

<H1 ALIGN=alignment > text
</H1>
 <H1 SRC=
<H1 SRC="URL" > text
</H1>
 <H1 DINGBAT=
<H1 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H1>
 <H1 NOWRAP>
<H1 NOWRAP> text </H1>
 <H1 CLEAR=
<H1 CLEAR=clear > text
</H1>
The heading 1 tag defines a level 1 heading. It is typically shown
in a very large bold font with several blank lines around it, and is
used by automatic
indexers to describe a page.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a graphic
image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic
entity to be embedded there. The clear attribute is
used to position a header after a graphic: it can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or ALL and specifies which margin
should be clear. The NOWRAP attribute prevents the
browser from breaking long header lines; use a BR tag to
break those lines yourself.
<H2> text </H2>

<H2 ALIGN=alignment > text
</H2>
 <H2 SRC=
<H2 SRC="URL" > text
</H2>
 <H2 DINGBAT=
<H2 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H2>
 <H2 NOWRAP>
<H2 NOWRAP> text </H2>
 <H2 CLEAR=
<H2 CLEAR=clear > text
</H2>
The heading 2 tag defines a level 2 heading. It is typically shown
in a large bold font with several blank lines around it.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a
graphic image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic entity to be embedded
there. The clear attribute is used to position a header
after a graphic: it can be LEFT, RIGHT, or
ALL and specifies which margin should be clear. The
NOWRAP attribute prevents the browser from breaking long header
lines; use a BR tag to break those lines yourself.
<H3> text </H3>

<H3 ALIGN=alignment >
text </H3>
 <H3 SRC=
<H3 SRC="URL" > text
</H3>
 <H3 DINGBAT=
<H3 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H3>
 <H3 NOWRAP>
<H3 NOWRAP> text </H3>
 <H3 CLEAR=
<H3 CLEAR=clear > text
</H3>
The heading 3 tag defines a level 3 heading. It is typically shown
in a large italic font, slightly indented, with blank lines around it.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a graphic
image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic
entity to be embedded there. The clear attribute is
used to position a header after a graphic: it can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or ALL and specifies which margin
should be clear. The NOWRAP attribute prevents the
browser from breaking long header lines; use a BR tag to
break those lines yourself.
<H4> text </H4>

<H4 ALIGN=alignment >
text </H4>
 <H4 SRC=
<H4 SRC="URL" > text
</H4>
 <H4 DINGBAT=
<H4 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H4>
 <H4 NOWRAP>
<H4 NOWRAP> text </H4>
 <H4 CLEAR=
<H4 CLEAR=clear > text
</H4>
The heading 4 tag defines a level 4 heading. It is typically shown
in a bold font, indented more than an level 3 heading, with blank
lines around it.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a graphic
image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic
entity to be embedded there. The clear attribute is
used to position a header after a graphic: it can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or ALL and specifies which margin
should be clear. The NOWRAP attribute prevents the
browser from breaking long header lines; use a BR tag to
break those lines yourself.
<H5> text </H5>

<H5 ALIGN=alignment >
text </H5>
 <H5 SRC=
<H5 SRC="URL" > text
</H5>
 <H5 DINGBAT=
<H5 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H5>
 <H5 NOWRAP>
<H5 NOWRAP> text </H5>
 <H5 CLEAR=
<H5 CLEAR=clear > text
</H5>
The heading 5 tag defines a level 5 heading. It is typically shown
in an italic font, indented the same as a level 4 heading, with a
blank line above it.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a graphic
image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic
entity to be embedded there. The clear attribute is
used to position a header after a graphic: it can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or ALL and specifies which margin
should be clear. The NOWRAP attribute prevents the
browser from breaking long header lines; use a BR tag to
break those lines yourself.
<H6> text </H6>

<H6 ALIGN=alignment >
text </H6>
 <H6 SRC=
<H6 SRC="URL" > text
</H6>
 <H6 DINGBAT=
<H6 DINGBAT="entity-name" >
text </H6>
 <H6 NOWRAP>
<H6 NOWRAP> text </H6>
 <H6 CLEAR=
<H6 CLEAR=clear > text
</H6>
The heading 6 tag defines a level 6 heading. It is typically shown
in a normal font, indented more than a level 5 heading, with a blank
line above it.
The alignment attribute can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER -- it defines the placement of
the header on the screen. The SRC attribute identifies a graphic
image to be embedded before the header text, while the
DINGBAT attribute identifies an iconic
entity to be embedded there. The clear attribute is
used to position a header after a graphic: it can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or ALL and specifies which margin
should be clear. The NOWRAP attribute prevents the
browser from breaking long header lines; use a BR tag to
break those lines yourself.
<HR>

<HR SRC= "URL">

<HR SIZE= number>

<HR WIDTH= number%>

<HR ALIGN= alignment%>

<HR NOSHADE>

<HR COLOR="colorname">
The horizontal rule tag causes a horizontal line to be drawn across
the screen. There is no </HR> tag.
The attributes allow you to specify the thickness of the line (in pixels)
with the SIZE attribute. The WIDTH attribute
governs what percentage of the screen width is occupied by the rule.
The ALIGN attribute aligns a rule that is smaller than
the screen: alignment can be LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER. The NOSHADE
attribute prevents the
browser from using any shading or three dimensional effects.
 The COLOR attribute allows you to change the colour of the text.
rrggbb is a six digit hexadecimal number with the first two
digits specifying the red value, the middle two the green value, and
the last two the blue value. Some sample colour values:
The COLOR attribute allows you to change the colour of the text.
rrggbb is a six digit hexadecimal number with the first two
digits specifying the red value, the middle two the green value, and
the last two the blue value. Some sample colour values:
- red
- FF0000
- green
- 00FF00
- blue
- 0000FF
- black
- 000000
- white
- FFFFFF
- grey
- 888888
- yellow
- FFFF00
- cyan
- 00FFFF
Colour names can also be used in the COLOR attribute.
Valid colours are: Aqua, Black, Blue, Fuchsia, Gray, Green, Lime,
Maroon, Navy, Olive, Purple, Red, Silver, Teal,Yellow, and White
 The SRC attribute specifies an
image file to be used for the rule.
The SRC attribute specifies an
image file to be used for the rule.
<BR>

<BR CLEAR>

<BR CLEAR="type">
The line break tag breaks the current line of text. It's not
necessary inside a
PRE element. There is no </BR> tag. The
CLEAR attribute type can be LEFT
to break until there is nothing to the left, RIGHT for
the right side, all for break until both sides are clear, and
NONE for a normal break.
<P> text
<P> text </P>

<P ALIGN=alignment>
text

<P NOWRAP> text
The paragraph tag starts a new paragraph, equivalent to two
BR tags. The </P> tag is optional if the
tag is only to insert space between two paragraphs, but vital when
attributes (for example, ALIGN="center") are to apply to
the whole paragraph. The ALIGN attribute can be one of LEFT,
RIGHT, or CENTER. The NOWRAP
attribute will make it so lines are only broken at the
<BR> tag.
<PLAINTEXT> text </PLAINTEXT>
The plain text tag defines text that should be shown in a
fixed width font with the line breaks and other
whitespace specified by the page author. There is no need to use
<BR> tags to indicate line breaks -- line breaks in
the source will be displayed by the browser. In addition multiple
spaces will be displayed as multiple spaces. HTML tags are not
rendered..
<PRE> text </PRE>
<PRE WIDTH=width> text
</PRE>
The preformatted text tag defines text that should be shown in a
fixed width font with the line breaks and other
whitespace specified by the page author. There is no need to use
<BR> tags to indicate line breaks -- line breaks in
the source will be displayed by the browser. In addition multiple
spaces will be displayed as multiple spaces. Typically used for
several lines of program code or for poetry. The width attribute
specifies the maximum number of characters per line.
|
